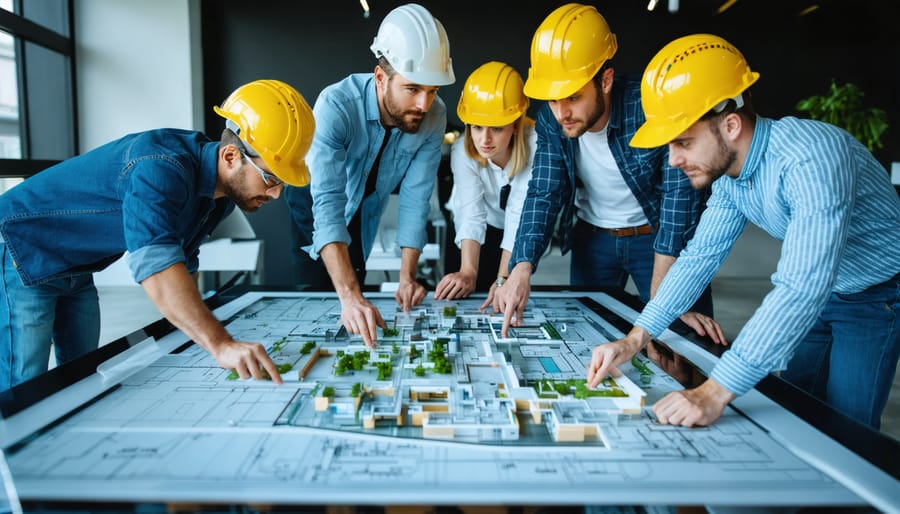
In today’s complex construction landscape, effective stakeholder engagement strategies determine the success or failure of major projects. Stakeholder collaboration transforms traditional project delivery by breaking down silos between owners, contractors, architects, and other key players, creating a unified approach to project execution. This integrated methodology has revolutionized how construction projects are conceived, planned, and delivered, reducing conflicts by up to 65% and accelerating project timelines by an average of 30%.
When project stakeholders align their objectives and work collaboratively, they create a powerful ecosystem that drives innovation, minimizes risks, and ensures optimal resource allocation. From initial concept development through final delivery, structured collaboration frameworks enable teams to leverage diverse expertise, anticipate challenges, and implement solutions proactively rather than reactively.
This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental principles of stakeholder collaboration in construction, providing practical insights for industry professionals seeking to enhance project outcomes through improved partnership strategies. We’ll examine proven methodologies, real-world case studies, and essential tools that enable successful stakeholder integration across all project phases.
Defining Stakeholder Collaboration in Construction
Key Stakeholders in Construction Projects
Construction projects involve a diverse network of stakeholders, each playing a crucial role in project success. Developers and project owners initiate the project vision and provide financial backing, establishing project objectives and success criteria. Their decisions significantly influence project scope, budget, and timeline parameters.
Architects and design professionals translate client requirements into viable designs, working closely with structural and mechanical engineers to ensure both aesthetic appeal and technical feasibility. These design teams must balance creative vision with practical constraints while adhering to regulatory requirements and sustainability goals.
General contractors serve as project orchestrators, managing day-to-day operations and coordinating various subcontractors. They bear primary responsibility for project execution, safety protocols, and quality control. Subcontractors, specialized in specific trades like electrical, plumbing, or HVAC, contribute their expertise to distinct project components.
Material suppliers and vendors form another critical stakeholder group, ensuring timely delivery of construction materials and equipment. Their reliability directly impacts project schedules and cost management.
End-users, whether future occupants or facility managers, provide valuable input regarding functionality and operational requirements. Their involvement during planning and design phases helps ensure the final product meets intended use specifications.
Local authorities and regulatory bodies, while external stakeholders, significantly influence project progress through permits, inspections, and compliance requirements. Their early engagement often prevents delays and ensures smooth project execution.
Understanding these stakeholder relationships and their interconnected roles is fundamental to achieving effective collaboration and project success.

The Evolution of Collaborative Practices
Stakeholder collaboration in construction has evolved significantly since the mid-20th century, transitioning from traditional hierarchical approaches to more integrated practices. In the 1960s and 1970s, project delivery typically followed a linear path, with minimal interaction between different parties. The 1980s marked a shift toward recognizing the value of cross-functional teams, though implementation remained limited.
The digital revolution of the 1990s catalyzed a major transformation in collaborative practices. The introduction of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and project management software enabled real-time communication and document sharing, fundamentally changing how stakeholders interact. By the early 2000s, integrated project delivery (IPD) emerged as a groundbreaking approach, emphasizing early involvement of all parties and shared risk/reward structures.
Today’s stakeholder collaboration is characterized by cloud-based platforms, mobile technologies, and virtual collaboration tools that enable seamless communication across geographical boundaries. Modern practices emphasize early stakeholder engagement, continuous feedback loops, and data-driven decision-making. This evolution reflects the industry’s growing understanding that successful project outcomes depend on effective coordination and communication among all participants, from owners and designers to contractors and end-users.
Core Components of Effective Stakeholder Collaboration
Communication Frameworks
Effective communication frameworks form the backbone of successful stakeholder collaboration in construction projects. These frameworks typically consist of structured protocols that define how information flows between different parties, ensuring clarity and accountability throughout the project lifecycle.
A well-designed communication framework incorporates multiple channels, including regular progress meetings, digital collaboration platforms, and formal documentation processes. Key elements include standardized reporting templates, clear escalation pathways for issues, and established feedback loops that enable continuous improvement.
Construction projects benefit from implementing both synchronous communication methods, such as real-time site meetings and video conferences, and asynchronous channels like project management software and email updates. This multi-channel approach ensures that stakeholders can access and share information effectively, regardless of their location or time zone.
The framework should also establish communication hierarchies, defining who needs to be informed about specific issues and when. This includes setting up emergency communication protocols for critical situations and regular update schedules for routine matters. By maintaining consistent communication standards, projects can minimize misunderstandings and keep all stakeholders aligned with project objectives.
Technology Integration
Modern stakeholder collaboration in construction projects relies heavily on advanced digital collaboration tools and integrated platforms. Building Information Modeling (BIM) serves as the cornerstone of technological integration, enabling real-time collaboration and visualization among multiple stakeholders. Cloud-based project management systems facilitate seamless document sharing, version control, and communication across teams, regardless of geographical locations.
Mobile applications and field management software empower on-site teams to update project status, share progress photos, and address issues instantly with office-based stakeholders. Virtual and augmented reality technologies allow stakeholders to experience and evaluate design options before construction begins, reducing costly changes during execution.
Collaborative dashboards provide centralized platforms for tracking project metrics, deadlines, and resource allocation, ensuring transparency and accountability. Integration of these tools with traditional project management methodologies creates a robust ecosystem that supports effective decision-making and maintains clear communication channels among all stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
Decision-Making Processes
Effective stakeholder collaboration relies on structured decision-making processes that ensure all voices are heard and considered. The construction industry typically employs a combination of consensus-building techniques and formal voting mechanisms to reach conclusive outcomes. Key methods include staged approvals, where stakeholders review and sign off on project milestones sequentially, and collaborative workshops that facilitate face-to-face problem-solving sessions. Project teams often utilize decision matrices to evaluate options against predetermined criteria, weighing factors such as cost, timeline, and environmental impact. Digital collaboration tools have modernized this process, enabling real-time input from remote stakeholders and creating transparent documentation trails. For complex decisions, many organizations implement a tiered approach, where routine decisions are handled at operational levels while strategic choices require broader stakeholder involvement and executive approval.
Benefits and Impact on Project Outcomes

Cost and Time Efficiency
Effective stakeholder collaboration directly impacts a project’s bottom line through significant cost savings and improved time management. One of the key benefits of effective stakeholder engagement is the reduction in costly rework and delays caused by miscommunication or conflicting objectives.
When stakeholders collaborate effectively, projects benefit from streamlined decision-making processes, reduced approval cycles, and better resource optimization. For example, early involvement of contractors and suppliers in the design phase can identify potential constructability issues before they become expensive problems during execution.
Research indicates that projects with strong stakeholder collaboration typically experience 20-30% reduced change orders and can achieve completion up to 15% faster than those with poor stakeholder integration. This efficiency stems from better coordination of workforce scheduling, equipment utilization, and material delivery timing. Additionally, collaborative approaches often lead to innovative solutions that can further reduce costs through value engineering and sustainable construction methods.
Risk Mitigation
Effective stakeholder collaboration serves as a powerful risk mitigation tool in construction projects by creating multiple layers of oversight and shared responsibility. When stakeholders work together closely, potential issues are identified earlier, allowing for proactive solutions rather than reactive crisis management. This collaborative approach enables better risk assessment through diverse perspectives and expertise.
Studies show that projects with strong stakeholder collaboration experience fewer costly delays and disputes. For instance, when designers, contractors, and suppliers coordinate during the pre-construction phase, they can identify constructability issues before they become expensive problems on-site. Regular stakeholder meetings and transparent communication channels help track potential risks and develop contingency plans collectively.
Risk sharing becomes more manageable through collaboration, as stakeholders can allocate responsibilities based on their expertise and capabilities. This distributed approach to risk management ensures that each party contributes to problem-solving while maintaining accountability for their scope of work. Additionally, documented collaborative processes create a clear audit trail for risk-related decisions, protecting all parties involved and facilitating more efficient dispute resolution when necessary.
Real-World Implementation Strategies
Implementing effective stakeholder collaboration in construction projects requires a structured and systematic approach. Begin by conducting a comprehensive stakeholder mapping exercise, identifying all key parties and their respective interests, influence levels, and potential contributions to the project. This initial assessment forms the foundation for developing targeted engagement strategies.
Establish clear communication protocols early in the project lifecycle. This includes setting up regular coordination meetings, creating standardized reporting templates, and implementing collaborative technology platforms that facilitate real-time information sharing. Building Information Modeling (BIM) tools, project management software, and digital collaboration platforms have proven particularly effective in fostering seamless stakeholder interaction.
Create a formal stakeholder engagement plan that outlines specific roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes. This document should detail escalation procedures, conflict resolution mechanisms, and key performance indicators for measuring collaboration effectiveness. Schedule regular stakeholder alignment sessions to review project progress, address concerns, and maintain strategic alignment.
Implement a transparent decision-making framework that considers input from all relevant stakeholders while maintaining project efficiency. This might involve establishing working groups for specific project aspects, utilizing consensus-building techniques, and documenting decision rationales for future reference.
Foster a collaborative culture by organizing team-building activities, cross-functional workshops, and joint problem-solving sessions. Encourage open dialogue and create safe spaces for stakeholders to voice concerns or suggest improvements. Regular feedback loops ensure continuous improvement in collaboration practices.
Maintain detailed documentation of stakeholder interactions, decisions, and outcomes. This creates accountability and provides valuable lessons learned for future projects. Remember that successful stakeholder collaboration is an iterative process that requires consistent monitoring and adjustment based on project needs and stakeholder feedback.
Stakeholder collaboration has emerged as a cornerstone of successful construction project delivery, transforming how industry professionals approach complex developments. Throughout this exploration, we’ve seen how effective collaboration drives innovation, reduces conflicts, and delivers superior project outcomes. The construction industry’s future increasingly depends on strengthening these collaborative relationships and leveraging new technologies to facilitate better communication and coordination.
As construction projects become more complex and sustainability requirements more stringent, the importance of stakeholder collaboration will only grow. Digital tools, BIM technology, and integrated project delivery methods are reshaping how stakeholders interact and share information, creating opportunities for more efficient and transparent collaboration.
Looking ahead, successful organizations will be those that embrace collaborative approaches and invest in developing their teams’ soft skills alongside technical capabilities. The industry trends point toward more integrated project teams, earlier stakeholder involvement, and increased use of collaborative contracts and delivery methods.
To remain competitive, construction professionals must prioritize relationship building, enhance their communication strategies, and adopt collaborative technologies. By fostering an environment of trust, transparency, and shared responsibility, organizations can better navigate challenges, accelerate innovation, and deliver projects that meet or exceed stakeholder expectations.
The future of construction lies in our ability to work together effectively, share knowledge openly, and maintain strong partnerships throughout the project lifecycle. As we continue to evolve and adapt to new challenges, stakeholder collaboration will remain fundamental to achieving project success and driving industry advancement.

