Construction risk management represents the strategic backbone of successful project delivery in today’s complex building environment. As construction projects grow increasingly sophisticated, implementing robust risk mitigation strategies has become paramount for protecting investments, ensuring safety, and maintaining project viability. This systematic approach encompasses identifying potential threats, quantifying their impact, and developing actionable responses across all project phases—from initial planning through final completion.
Modern construction risk management integrates advanced analytics, real-time monitoring systems, and comprehensive stakeholder collaboration to address challenges before they escalate into costly setbacks. By combining traditional risk assessment methodologies with emerging technologies, construction professionals can now predict, prevent, and respond to risks with unprecedented precision, ultimately safeguarding project outcomes and stakeholder interests. This proactive stance not only minimizes potential losses but also optimizes resource allocation, enhances safety protocols, and ensures regulatory compliance in an increasingly regulated industry landscape.
Understanding Construction Risk Categories
Technical and Design Risks
Technical and design risks pose significant challenges in construction projects, often stemming from incomplete drawings, design errors, or engineering miscalculations. These risks can manifest as structural integrity issues, incompatible building systems, or code compliance problems. Common technical risks include foundation design flaws, inadequate load calculations, and MEP system conflicts. Design risks frequently emerge from poor coordination between different design disciplines or incomplete site investigations.
To mitigate these risks, firms increasingly employ Building Information Modeling (BIM) for clash detection and virtual construction simulation. Regular design reviews, third-party validation, and constructability assessments are essential preventive measures. Engineering teams must also consider site-specific conditions, local building codes, and material specifications to ensure design feasibility.
The implementation of rigorous quality control processes and systematic design verification protocols helps identify potential issues before they impact construction. Early involvement of construction teams in the design phase can provide valuable insights into practical challenges and potential solutions.
Financial and Economic Risks
Financial and economic risks represent significant challenges in construction projects, often manifesting as budget overruns, unexpected cost escalations, and market volatility. Project stakeholders must carefully monitor material price fluctuations, labor costs, and interest rate changes that can impact project viability. Effective risk mitigation requires robust financial planning, contingency budgets, and regular cost tracking. Construction managers face various cost management challenges including supply chain disruptions, currency exchange fluctuations, and inflation impacts. Implementing comprehensive financial controls, maintaining adequate cash flow, and securing appropriate insurance coverage are essential strategies for protecting project investments and ensuring financial stability throughout the construction lifecycle.
Environmental and Safety Risks
Environmental and safety risks represent critical challenges in construction projects that demand rigorous management protocols. Project managers must ensure compliance with OSHA regulations, environmental protection standards, and local building codes while implementing comprehensive construction safety essentials. Key considerations include hazardous material handling, air and noise pollution control, waste management, and worker safety protocols. Environmental impact assessments must be conducted before project initiation, while regular safety audits and training programs help maintain workplace safety standards. Successful risk management in this area requires proactive measures, including proper personal protective equipment (PPE) provision, regular site inspections, and maintaining detailed documentation of safety procedures and environmental compliance measures.

Risk Assessment and Identification Process
Risk Assessment Tools and Techniques
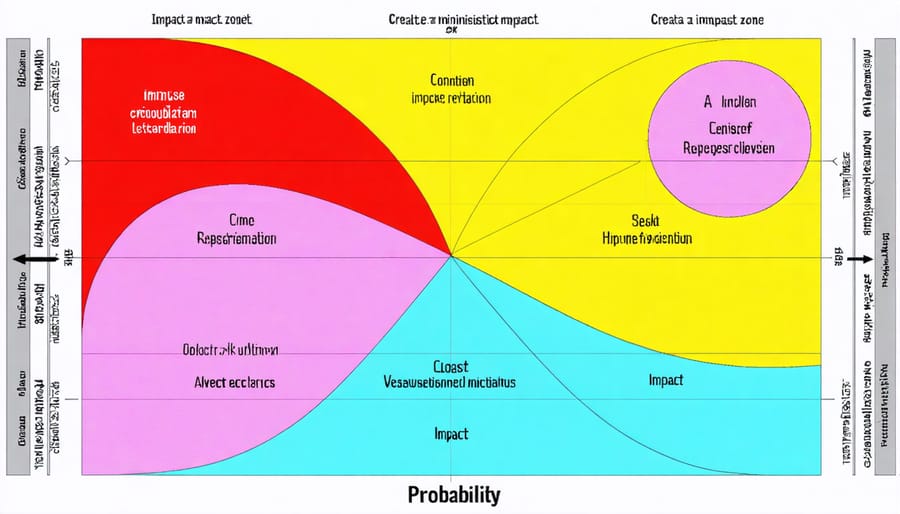
Construction professionals utilize various tools and techniques to systematically evaluate and quantify project risks. Risk matrices serve as fundamental visual tools, typically displaying probability on one axis and impact severity on the other, enabling teams to prioritize risks effectively. These matrices commonly use color coding (red, yellow, green) to indicate risk levels and guide resource allocation.
Probability assessments employ both qualitative and quantitative methods to determine the likelihood of risk occurrence. Teams analyze historical data, expert opinions, and market conditions to assign probability ratings, often using scales from 1-5 or percentages. This data-driven approach ensures more accurate risk prediction and helps in developing appropriate mitigation strategies.
Impact analysis methods focus on evaluating potential consequences across multiple parameters, including cost, schedule, quality, and safety. Monte Carlo simulation stands out as a sophisticated technique, allowing teams to model various scenarios and their potential outcomes. Additionally, fault tree analysis helps identify root causes and potential failure points in construction processes.
Modern risk assessment incorporates specialized software tools that integrate these techniques, providing real-time risk monitoring and automated alerts. These platforms often feature customizable risk registers, automated scoring systems, and trend analysis capabilities, enabling project teams to maintain dynamic risk profiles throughout the construction lifecycle. Regular reviews and updates of risk assessments ensure that emerging threats are identified and addressed promptly.
Early Warning Signs and Red Flags
Recognizing early warning signs in construction projects is crucial for effective risk management. These indicators often appear subtly at first but can escalate into significant issues if left unaddressed. Key financial red flags include unexpected cost overruns, delayed payments, or frequent budget revision requests. When subcontractors begin requesting accelerated payment schedules or showing signs of financial strain, this often signals deeper project issues.
Schedule-related warning signs manifest through missed milestones, frequent requests for timeline extensions, or delays in material deliveries. Pay particular attention to patterns of workforce inconsistency, including high turnover rates or irregular attendance, as these often precede major project disruptions.
Quality concerns may emerge through increased rework requests, failed inspections, or deviation from specified materials. Documentation irregularities, such as incomplete daily reports or missing permits, can indicate compliance risks and potential legal exposure.
Communication breakdown presents another critical warning sign. Watch for patterns of missed meetings, delayed responses to RFIs (Requests for Information), or increasing conflicts between project stakeholders. Environmental red flags include unexpected site conditions, regulatory compliance issues, or community complaints.
Modern construction management platforms can help track these indicators through data analytics and automated alerts. Project managers should establish clear protocols for flagging and escalating these warning signs, ensuring swift intervention before they develop into major obstacles that threaten project success.
Implementing Risk Mitigation Strategies
Risk Transfer Methods
Risk transfer is a critical component of construction risk management, involving the strategic allocation of risks to parties best equipped to handle them. Insurance represents the primary method of risk transfer in construction projects, with comprehensive coverage options including builder’s risk insurance, professional liability insurance, and general liability coverage protecting against various project-related exposures.
Contractual arrangements serve as another crucial risk transfer mechanism. Well-structured contracts clearly delineate responsibilities and liabilities among project stakeholders, including owners, contractors, subcontractors, and design professionals. Key contractual provisions typically address indemnification clauses, warranty obligations, and limitation of liability terms, establishing a framework for risk allocation.
Risk sharing through joint ventures and partnerships enables multiple parties to distribute both potential losses and rewards. This approach is particularly effective for large-scale projects where the risk exposure might be too substantial for a single entity to bear. Performance bonds and payment bonds provide additional security layers, ensuring project completion and protecting against contractor default.
Modern construction projects increasingly employ integrated project delivery (IPD) methods, which facilitate collaborative risk sharing among team members. This approach aligns with the industry’s shift toward more cooperative project delivery models, where risks and rewards are distributed based on predetermined agreements.
The success of risk transfer strategies depends on careful documentation, clear communication, and thorough understanding of insurance policies and contractual obligations. Regular review and updates of risk transfer mechanisms ensure their continued effectiveness throughout the project lifecycle, adapting to changing project conditions and emerging risks.
Risk Reduction Techniques
Effective risk reduction in construction projects requires a systematic approach combining preventive measures and strategic planning. The first crucial step is implementing robust safety protocols and training programs for all personnel, ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. Regular safety audits and inspections help identify potential hazards before they materialize into problems.
Risk transfer through appropriate insurance coverage and contractual arrangements provides essential protection. However, it’s equally important to establish clear responsibility matrices and accountability frameworks among project stakeholders. Detailed documentation and communication protocols help minimize misunderstandings that could lead to disputes or delays.
Quality control measures, including material testing and workmanship inspections, significantly reduce construction defect risks. Implementing a comprehensive quality management system with regular checkpoints throughout the project lifecycle ensures early detection of issues.
Financial risk reduction involves careful cash flow management, establishing contingency reserves, and maintaining strong relationships with reliable suppliers and subcontractors. Regular project cost reviews and earned value analysis help identify potential budget overruns early.
Technology plays a crucial role in modern risk reduction. Building Information Modeling (BIM) helps identify spatial conflicts before construction begins. Project management software enables better schedule control and resource allocation, while real-time monitoring systems track site conditions and equipment performance.
Weather-related risks can be mitigated through careful project scheduling and implementing protective measures during adverse conditions. Additionally, maintaining a flexible project timeline with built-in buffer periods helps absorb unexpected delays without compromising overall project delivery.
Regular stakeholder meetings and progress reviews ensure alignment of expectations and early identification of potential issues, allowing for proactive rather than reactive risk management.
Technology and Risk Management
Digital Risk Management Platforms
Modern construction projects increasingly rely on digital risk management solutions to streamline risk identification, assessment, and mitigation processes. These platforms integrate multiple risk management functions into centralized dashboards, enabling real-time monitoring and response to potential threats.
Key features typically include automated risk assessment tools, predictive analytics for early warning detection, and collaborative workflows that facilitate communication between stakeholders. Construction teams can track safety incidents, monitor compliance requirements, and manage insurance documentation through unified interfaces.
Advanced platforms incorporate machine learning algorithms to analyze historical project data, identifying patterns and potential risk factors before they escalate into significant issues. Cloud-based systems ensure that risk-related information is accessible to authorized team members across different locations, promoting transparency and informed decision-making.
These digital solutions also provide robust reporting capabilities, allowing project managers to generate detailed risk analysis reports, track mitigation efforts, and demonstrate regulatory compliance. By automating routine risk management tasks, these platforms help construction teams focus on strategic risk mitigation while maintaining comprehensive documentation for audit purposes.
Data Analytics in Risk Prevention
Data analytics has revolutionized construction risk management by enabling predictive insights and proactive decision-making. Through the collection and analysis of vast amounts of project data, construction firms can now identify potential risks before they materialize. Advanced analytics platforms process information from multiple sources, including historical project data, sensor readings, weather patterns, and workforce performance metrics.
Machine learning algorithms analyze this data to detect patterns and correlations that might indicate emerging risks. For instance, by analyzing equipment sensor data, teams can predict potential mechanical failures before they cause costly delays. Similarly, weather data analysis helps optimize scheduling and minimize weather-related disruptions.
Real-time monitoring systems provide immediate insights into project progress, safety conditions, and resource utilization. These systems can trigger automatic alerts when key risk indicators exceed predetermined thresholds, allowing project managers to intervene promptly. Moreover, predictive analytics help in resource allocation, budget forecasting, and schedule optimization by identifying potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
By leveraging big data analytics, construction companies can develop more accurate risk assessments, implement targeted mitigation strategies, and significantly improve project outcomes while reducing unexpected complications.
In today’s complex construction landscape, effective risk management is not merely an option but a fundamental necessity for project success. Throughout this comprehensive examination of construction risk management, we’ve explored the multifaceted approaches and strategies that industry professionals must employ to safeguard their projects against potential threats and uncertainties.
The key takeaway is that successful construction risk management requires a systematic, proactive approach that encompasses identification, assessment, mitigation, and continuous monitoring of risks. By implementing robust risk management frameworks, construction companies can significantly reduce project delays, cost overruns, and safety incidents while improving overall project outcomes.
We’ve seen how modern technology and digital tools have revolutionized risk management practices, enabling real-time monitoring, data-driven decision-making, and improved collaboration among stakeholders. However, it’s crucial to remember that technology alone cannot guarantee success – it must be combined with experienced judgment, clear communication protocols, and well-defined risk management procedures.
The importance of early risk identification and assessment cannot be overstated. Projects that incorporate risk management from the planning phase consistently demonstrate better performance metrics and higher success rates. Furthermore, maintaining detailed documentation and establishing clear lines of responsibility ensures that risk management remains an active, ongoing process throughout the project lifecycle.
Looking ahead, the construction industry faces evolving challenges, from climate change considerations to supply chain disruptions and skilled labor shortages. Organizations that prioritize and continuously refine their risk management strategies will be better positioned to navigate these challenges successfully.
Remember that effective risk management is not about eliminating all risks – an impossible task in construction – but about understanding, preparing for, and actively managing potential threats while maximizing opportunities. By fostering a risk-aware culture and implementing comprehensive risk management practices, construction professionals can deliver projects that meet quality standards, timeline requirements, and budget constraints while ensuring the safety and satisfaction of all stakeholders involved.

