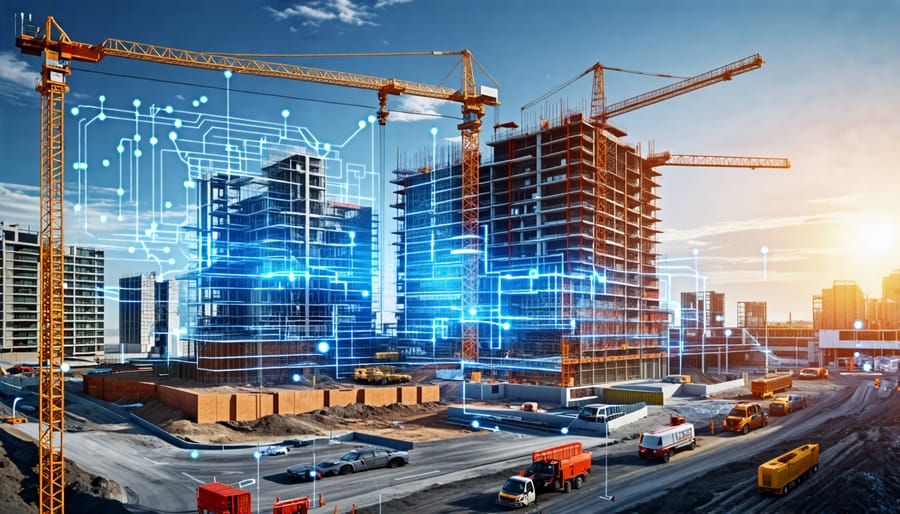
Discover how digital twins are revolutionizing the construction industry, enabling smarter planning, efficient execution, and optimized asset management. In this article, we delve into the concept of digital twins, exploring their key components, real-world applications, and the immense potential they hold for construction projects of all scales. Through expert insights and in-depth case studies, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of how digital twins are transforming the way we design, build, and maintain the built environment. Prepare to embark on a journey that will change your perspective on the future of construction and unlock new possibilities for your projects.
What is a Digital Twin?

Key Components of a Digital Twin
The key components of a digital twin in construction include 3D models, real-time data, and simulation capabilities. The foundation of a digital twin is a highly accurate, detailed 3D representation of the physical asset, created using technologies such as BIM (Building Information Modeling) and laser scanning. This model serves as a virtual replica of the building or infrastructure project, capturing its geometry, materials, and spatial relationships.
Real-time data is another crucial element of a digital twin. Sensors installed on the physical asset collect data on various parameters, such as temperature, humidity, energy consumption, and structural performance. This data is continuously streamed to the digital twin, enabling it to mirror the real-world behavior and conditions of the asset in near real-time.
Simulation capabilities are the third key component of a digital twin. By integrating the 3D model with real-time data and advanced simulation algorithms, a digital twin can predict the performance of the asset under different scenarios. This allows construction professionals to test design options, optimize energy efficiency, and identify potential issues before they occur in the physical world. Simulations can also help in planning maintenance activities and extending the life span of the asset.
These key components – 3D models, real-time data, and simulation capabilities – work together to create a powerful tool for construction professionals. By providing a comprehensive, dynamic view of the asset throughout its lifecycle, a digital twin enables data-driven decision making, risk mitigation, and performance optimization.
How Digital Twins Differ from Traditional BIM
While digital twins and Building Information Modeling (BIM) both involve digital representations of buildings, they have distinct differences. BIM primarily focuses on the design and construction phases, providing a static 3D model with detailed information about the building’s components, materials, and geometry. In contrast, digital twins are dynamic, real-time replicas that continue to evolve throughout the entire lifecycle of the building, from conception to demolition. Digital twins incorporate live data from sensors, IoT devices, and other sources to mirror the physical asset’s performance, enabling real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization. Additionally, digital twins can simulate various scenarios, predict future performance, and support data-driven decision-making, whereas BIM models are typically used for visualization, coordination, and documentation purposes. In summary, digital twins extend beyond the capabilities of traditional BIM by offering a living, interactive, and predictive representation of the built environment.
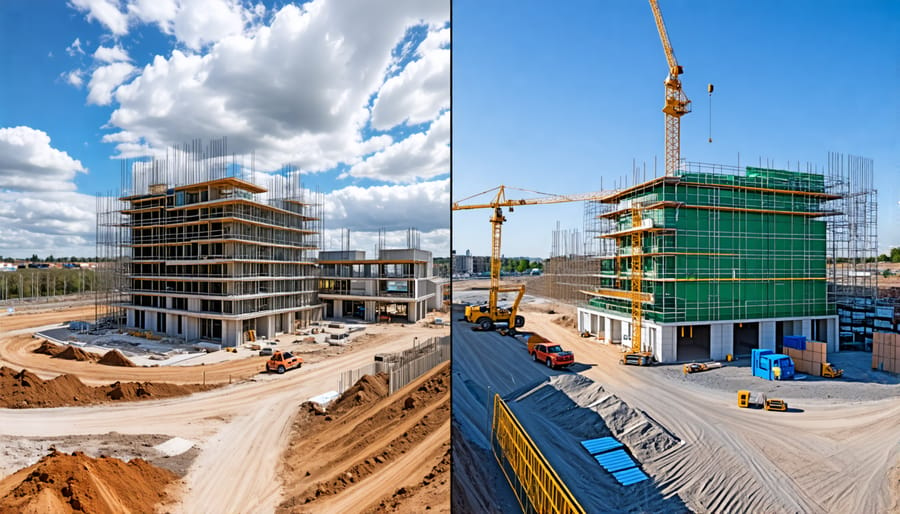

Applications of Digital Twins in Construction
Design and Planning
Digital twins play a crucial role in the design and planning phases of construction projects. By creating a virtual representation of the proposed structure, architects and engineers can iterate on designs, test different scenarios, and optimize the building’s performance before breaking ground. This allows for more efficient and cost-effective decision-making, reducing the likelihood of costly changes later in the project.
Digital twins also facilitate collaboration among project stakeholders. By providing a shared, interactive platform, digital twins enable architects, engineers, contractors, and clients to visualize and explore the design together. This improved communication and coordination helps ensure that everyone is aligned on the project’s goals and requirements.
Moreover, digital twins can integrate data from various sources, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), geographic information systems (GIS), and site surveys. This integration allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the project’s context, enabling better-informed design decisions and more accurate planning.
Throughout the design and planning process, digital twins can be used to simulate various aspects of the building’s performance, such as energy efficiency, lighting, and acoustics. These simulations help optimize the design for improved occupant comfort, reduced environmental impact, and lower operating costs over the building’s lifecycle.
Construction Monitoring and Management
Digital twins enable construction professionals to monitor and manage ongoing projects in real-time, optimizing efficiency and reducing risks. By integrating IoT sensors, drones, and other data capture technologies, digital twins provide a continuous stream of information about the construction site. This data is then processed and visualized within the digital twin platform, allowing project managers to track progress, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions. For example, real-time monitoring of equipment usage and worker productivity can help optimize resource allocation and prevent delays. Digital twins also facilitate collaboration among stakeholders, as everyone can access the same up-to-date information and communicate effectively. Furthermore, by simulating various scenarios and testing alternative approaches, digital twins enable proactive problem-solving and risk mitigation. This predictive capability helps construction teams stay on schedule, within budget, and in compliance with quality and safety standards. As the project progresses, the digital twin evolves alongside the physical asset, ensuring that the virtual model remains an accurate representation of reality. This dynamic nature of digital twins empowers construction professionals to make data-driven decisions throughout the project lifecycle, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes.
Facility Operations and Maintenance
Digital twins play a crucial role in streamlining facility management and maintenance processes after construction is complete. By leveraging the real-time data and insights provided by the digital twin, facility managers can optimize operations, reduce maintenance costs, and extend the lifespan of the building. The digital twin serves as a centralized repository of information, enabling facility managers to access up-to-date data on building systems, equipment performance, and energy consumption. This data-driven approach allows for predictive maintenance, where potential issues can be identified and addressed before they escalate into costly repairs. Additionally, the digital twin can simulate various scenarios, such as emergency response plans or energy optimization strategies, helping facility managers make informed decisions and improve overall operational efficiency. By integrating IoT sensors and real-time monitoring, the digital twin continuously updates itself, ensuring that the virtual model accurately reflects the physical building throughout its lifecycle. This ongoing synchronization between the digital twin and the physical asset empowers facility managers to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource allocation, and enhance the overall performance and sustainability of the building.
Case Studies
Case Study 1
The Crossrail project in London, one of Europe’s largest infrastructure projects, successfully implemented digital twins to streamline construction and improve efficiency. By creating a virtual replica of the entire railway system, including tunnels, stations, and associated infrastructure, the project team could simulate and analyze various scenarios, identify potential issues, and optimize designs before physical construction began. This proactive approach enabled them to anticipate and mitigate risks, reduce rework, and enhance collaboration among stakeholders. The digital twin also facilitated real-time monitoring of progress, allowing for swift decision-making and adaptations to changing circumstances. As a result, the Crossrail project benefited from improved safety, reduced costs, and increased productivity. The digital twin continues to serve as a valuable asset for ongoing maintenance and future upgrades, demonstrating the long-term value of this technology in the construction industry.
Case Study 2
The Hickory Construction Company recently employed digital twin technology for a large-scale mixed-use development project. By creating a comprehensive digital replica of the entire construction site, the company was able to streamline project management, enhance collaboration among stakeholders, and optimize resource allocation. The digital twin incorporated real-time data from sensors, drones, and other IoT devices, enabling the team to monitor progress, identify potential issues, and make data-driven decisions. This application of digital twin technology resulted in a 15% reduction in construction time, a 12% decrease in material waste, and improved overall project efficiency. The Hickory Construction Company’s success demonstrates the tangible benefits of leveraging digital twins in the construction industry, setting a new standard for project management and delivery.
Moreover, the digital twin allowed for seamless communication between the design team, contractors, and suppliers, ensuring that everyone was working with the most up-to-date information. The ability to visualize the project in a virtual environment facilitated better decision-making, as stakeholders could explore various scenarios and optimize designs before implementation. This proactive approach minimized the need for costly rework and change orders, ultimately saving the company both time and money. The Hickory Construction Company’s case study serves as a compelling example of how digital twin technology can revolutionize the way construction projects are planned, executed, and managed, paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable future in the industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital twins are revolutionizing the construction industry by enabling a more efficient, collaborative, and data-driven approach to project planning, execution, and management. By creating virtual replicas of physical assets, digital twins allow stakeholders to visualize, simulate, and optimize every aspect of a construction project, from design and engineering to operations and maintenance. The integration of IoT sensors, BIM, and advanced analytics empowers construction professionals to make informed decisions, reduce risks, and improve overall project outcomes. Real-world case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits of digital twins, such as cost savings, reduced delays, enhanced safety, and improved sustainability. As the construction industry continues to embrace digital transformation, the adoption of digital twins is expected to grow, unlocking new opportunities for innovation and collaboration. With the power to bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds, digital twins are set to become an essential tool for construction professionals seeking to stay competitive in an increasingly complex and dynamic industry. By harnessing the potential of digital twins, the construction sector can build smarter, faster, and more sustainably, ultimately shaping the future of our built environment.

