The integration of smart home features has become a cornerstone of modern construction, transforming how we approach residential development. Industry data reveals that 63% of new construction projects now incorporate automated systems from the ground up, marking a pivotal shift in building methodology.
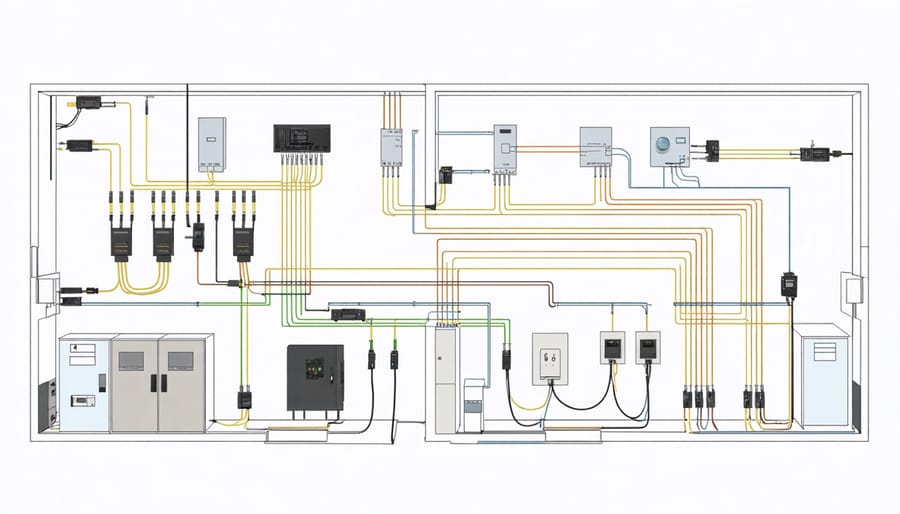
Pre-wire strategic locations during the framing stage to accommodate future technological upgrades, including dedicated conduits for fiber optics, power-over-ethernet cables, and distributed antenna systems. Design centralized equipment rooms with adequate ventilation and power requirements, ensuring scalability for expanding smart systems. Implement structured wiring protocols that exceed current standards, incorporating Cat-6A or fiber optic cabling throughout the structure to support bandwidth-intensive applications.
Construction professionals must now balance architectural integrity with technological infrastructure, considering factors like RF signal penetration, power distribution networks, and environmental control systems during the initial design phase. This strategic approach to smart home construction not only enhances property values but also positions developments at the forefront of residential innovation, meeting the growing demand for intelligent living spaces in the contemporary market.
The key to successful smart home implementation lies in creating a robust foundation that anticipates future technological advancements while maintaining flexibility for system upgrades and modifications throughout the building’s lifecycle.
Core Infrastructure Requirements
Structured Wiring Systems
Structured wiring systems form the backbone of any smart home installation, requiring careful planning and implementation during the construction phase. A robust infrastructure typically includes Category 6a (Cat6a) or Category 7 ethernet cables, providing bandwidth capabilities up to 10 Gbps and ensuring future-proof connectivity for emerging technologies.
The system should incorporate a centralized distribution panel, typically located in a dedicated technical room or basement, where all cables terminate. This panel houses network switches, routers, and other essential equipment. For optimal performance, maintain separate conduits for low-voltage and high-voltage cables to prevent electromagnetic interference.
Power distribution requires strategic placement of electrical outlets and dedicated circuits for high-demand smart devices. Include surge protection at the main panel and consider implementing a whole-house UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) system to maintain critical smart home functions during power outages.
Cable management solutions should include:
– Horizontal and vertical cable pathways
– Access points in each room for future expansion
– Service loops at termination points
– Labeled cables for easy identification
– Proper bend radius protection
For wireless coverage optimization, install ethernet drops in ceiling locations for wireless access points, ensuring comprehensive WiFi coverage throughout the property. Include additional cables for security cameras, smart displays, and automation controllers. Documentation of the complete wiring infrastructure is essential for future maintenance and upgrades.
Wireless Network Planning
Effective wireless network planning is crucial for smart home functionality and requires careful consideration of coverage, capacity, and signal strength. A comprehensive site survey should be conducted during the pre-construction phase to identify potential dead zones and interference sources, enabling optimal access point placement.
For multi-story residences, strategic placement of wireless access points on each floor ensures consistent coverage. Consider installing access points in central locations, typically one per 1,500 square feet, accounting for wall materials and structural elements that may impact signal penetration. Metal studs, concrete walls, and certain types of insulation can significantly attenuate wireless signals.
Mesh network systems have become increasingly popular for larger homes, offering seamless coverage through multiple interconnected nodes. These systems automatically route traffic through the most efficient path and provide self-healing capabilities if one node fails. When implementing mesh networks, position satellite nodes within 30-50 feet of each other for optimal performance.
To maximize signal penetration, consider incorporating CAT6 or CAT6A cable runs during construction to support wired backhaul for mesh systems. This approach reduces wireless congestion and ensures more stable connections for bandwidth-intensive smart devices.
For optimal performance, segment networks to separate IoT devices from primary networks, enhancing both security and network efficiency. Plan for future expansion by including additional ethernet drops in strategic locations and selecting enterprise-grade equipment that supports the latest wireless standards.

Key Smart Home Systems Integration
HVAC and Energy Management
Modern HVAC and energy management systems form the backbone of smart home climate control, offering unprecedented efficiency and comfort. Advanced smart thermostats, equipped with AI-driven learning capabilities, can analyze occupancy patterns and adjust temperature settings automatically, resulting in energy savings of up to 23% annually according to recent industry studies.
Integration with zonal control systems allows for precise temperature management across different areas of the home, eliminating the inefficiencies of traditional single-thermostat setups. Smart sensors continuously monitor humidity, CO2 levels, and air quality, triggering automated responses through connected ventilation systems.
Real-time energy consumption monitoring provides homeowners with detailed insights through mobile applications, enabling data-driven decisions about energy usage. These systems can automatically adjust HVAC operations based on utility pricing schedules, weather forecasts, and peak demand periods.
Recent innovations include predictive maintenance capabilities that utilize machine learning algorithms to detect potential system failures before they occur. This proactive approach significantly reduces maintenance costs and extends equipment lifespan. Integration with smart window systems and automated shade controls further optimizes natural heating and cooling, creating a comprehensive climate management solution that balances comfort with energy efficiency.
Security and Access Control
Security and access control systems form the cornerstone of modern smart home implementation, combining sophisticated hardware with intelligent software solutions. Smart locks with biometric authentication and remote access capabilities have become standard installations, offering multiple entry methods while maintaining robust security protocols. These systems can integrate with mobile devices, allowing homeowners to grant temporary access to service providers or guests through time-limited digital keys.
Surveillance systems have evolved beyond basic CCTV setups to include AI-powered cameras with motion detection, facial recognition, and real-time alerts. Professional installations typically incorporate weatherproof outdoor cameras with night vision capabilities, alongside indoor units strategically placed at entry points and high-traffic areas. These systems can be programmed to distinguish between regular household members and unknown visitors, reducing false alerts.
Automated security features extend to window sensors, glass break detectors, and doorbell cameras, all connected through a central hub that enables comprehensive monitoring. Integration with home automation platforms allows for sophisticated security scenarios, such as automatically activating exterior lights when motion is detected or recording video clips when doors are opened during specified hours.
For maximum effectiveness, these systems should be planned during the initial construction phase, allowing for proper cable routing and power supply installation. This approach ensures clean aesthetics and optimal performance while reducing future maintenance requirements. Regular software updates and professional monitoring services can further enhance the system’s reliability and response capabilities.
Lighting and Shade Control
Modern lighting and shade control systems represent a cornerstone of smart home infrastructure, offering unprecedented control over ambient conditions while delivering substantial energy savings. Advanced lighting management systems utilize networked LED fixtures, occupancy sensors, and daylight harvesting technology to automatically adjust illumination levels based on natural light availability and room usage patterns.
Integration of smart shading solutions with lighting controls creates a synchronized ecosystem that optimizes both natural and artificial light. Motorized shade systems can be programmed to respond to sunlight intensity, time of day, and seasonal variations, working in tandem with lighting controls to maintain optimal indoor conditions while implementing powerful energy efficiency solutions.
The implementation requires careful consideration of control protocols, with options including DALI, DMX, and wireless standards like Zigbee or Z-Wave. Each offers distinct advantages for different project scales and requirements. For maximum effectiveness, lighting zones should be mapped according to space usage patterns and daylight availability, with careful attention to sensor placement and calibration.
Real-time monitoring and data analytics capabilities enable facility managers to track energy consumption patterns and optimize system performance. Advanced systems can integrate with building management platforms, allowing for centralized control and automated responses to changing environmental conditions, ultimately reducing operational costs while enhancing occupant comfort and productivity.
Future-Proofing Considerations
Scalable Infrastructure Design
When designing smart home infrastructure, scalability must be a cornerstone principle of modern construction integration. The foundation of a scalable system begins with implementing a robust networking infrastructure that can accommodate future technological advancements and increased device loads.
Key considerations include installing high-capacity electrical systems with dedicated circuits for smart devices, implementing structured cabling with CAT6A or fiber optic solutions, and establishing multiple wireless access points strategically positioned throughout the structure. These elements create a framework that supports both current requirements and future expansion.
The implementation of distributed architecture proves essential, utilizing multiple smart home controllers or hubs rather than relying on a single point of control. This approach ensures system reliability while facilitating seamless integration of additional devices and subsystems as technology evolves.
Spaces designated for future technology integration should be incorporated into the initial design phase. This includes dedicated equipment rooms, accessible cable pathways, and power provisions in anticipated expansion areas. The integration of universal protocols and standards, such as Matter and Thread, ensures long-term compatibility with emerging technologies.
Professional system documentation and clearly labeled infrastructure components are crucial for successful scaling. This documentation should include detailed network topology maps, cable schedules, and expansion zone designations, enabling efficient system modifications and upgrades as client needs evolve.
Interoperability Standards
Interoperability remains a critical factor in smart home implementation, with industry standards playing a pivotal role in ensuring seamless device integration and system functionality. Leading protocols such as Matter, developed by the Connectivity Standards Alliance, have emerged as game-changers by providing a unified communication framework that enables devices from different manufacturers to work together effectively.
Project managers must carefully consider protocol selection during the planning phase. Currently, Matter, Zigbee, and Z-Wave dominate the market, each offering distinct advantages. Matter, being the newest standard, promises broader compatibility across major technology ecosystems, while Zigbee and Z-Wave have established track records in reliability and security.
According to industry data, implementing universal protocols can reduce integration costs by up to 30% and significantly decrease post-installation troubleshooting time. Construction professionals should ensure that selected devices support at least one major protocol and maintain compatibility with popular smart home platforms like Google Home, Amazon Alexa, or Apple HomeKit.
For optimal interoperability, consider implementing a hub-based architecture that can bridge different protocols. This approach provides flexibility for future expansions and upgrades while maintaining system stability. Additionally, documenting protocol choices and creating detailed integration maps helps facilitate smooth handovers to property owners and maintenance teams.
Networking infrastructure must support these protocols through proper Wi-Fi coverage, ethernet backbone installation, and adequate bandwidth allocation. This foundation ensures reliable communication between devices and maintains system performance as the smart home ecosystem grows.
Cost-Benefit Analysis

Initial Investment vs. Long-term Returns
While the initial investment in smart home technology can be substantial, ranging from $15,000 to $50,000 for comprehensive systems in new construction projects, the long-term returns justify the upfront costs. Analysis of smart building metrics indicates that integrated smart systems can reduce energy consumption by 30-40% annually. This translates to significant operational cost savings over the building’s lifecycle.
Property valuations demonstrate that smart homes command a 3-7% premium in the market, with high-end implementations yielding returns up to 11% above comparable traditional properties. Energy management systems, typically costing $5,000-$10,000 to implement, can achieve ROI within 3-5 years through reduced utility expenses and increased operational efficiency.
Additionally, smart home features contribute to lower insurance premiums, with some providers offering discounts of up to 20% for properties equipped with advanced security and monitoring systems. When factoring in reduced maintenance costs and extended equipment lifespans through predictive maintenance, the total return on investment typically materializes within 5-7 years of implementation.
Market Value Impact
Recent market analyses indicate that smart home integration can increase property values by 3-7% on average, with luxury properties seeing potential increases of up to 11%. This significant value proposition stems from the growing demand for connected, energy-efficient homes among modern buyers.
Studies from leading real estate firms demonstrate that properties equipped with integrated smart systems typically sell 20-30 days faster than comparable traditional homes. Key value-driving features include comprehensive home automation systems, advanced security solutions, and energy management platforms that deliver measurable cost savings.
Property appraisers increasingly factor smart technology infrastructure into their valuations, particularly emphasizing systems that enhance energy efficiency, security, and overall home management capabilities. The presence of structured wiring, dedicated networking spaces, and whole-home automation systems has become a significant differentiator in competitive markets.
For developers and contractors, incorporating smart home technology during the construction phase proves more cost-effective than retrofitting, offering better returns on investment. Additionally, properties with documented energy savings through smart systems command premium prices, with buyers willing to pay more for homes that demonstrate reduced operational costs and enhanced sustainability credentials.
As we look to the future of residential construction, smart home integration has evolved from a luxury option to an essential consideration in modern building practices. The convergence of IoT technology, sustainable building practices, and growing consumer demand has created a transformative shift in how we approach home construction.
The key takeaways from our analysis demonstrate that successful smart home implementation requires careful planning from the earliest stages of construction. This includes designing adaptable infrastructure, implementing robust networking capabilities, and ensuring seamless integration of various smart systems. Construction professionals must prioritize scalability and future-proofing in their designs to accommodate emerging technologies and changing homeowner needs.
Industry trends suggest that the smart home market will continue its explosive growth, with particular emphasis on energy management, security systems, and automated environmental controls. Construction firms that develop expertise in smart home integration now will be better positioned to meet future market demands and maintain competitive advantage.
Looking ahead, we can expect to see increased standardization of smart home protocols, improved interoperability between devices, and more sophisticated AI-driven home management systems. The construction industry must remain adaptable and forward-thinking, investing in training and partnerships with technology providers to stay ahead of these developments.
Success in this evolving landscape will depend on balancing technological innovation with practical implementation, ensuring that smart home features enhance rather than complicate the living experience. As construction professionals, our role is to create homes that are not just smart, but intelligent in their design, efficient in their operation, and valuable to their occupants.

